AI Flows are visual pipelines that automate multi-step AI tasks. Connect data sources, processing nodes, AI models, and outputs in a drag-and-drop canvas. No coding required.
Example: Web scraping and feature extraction flow
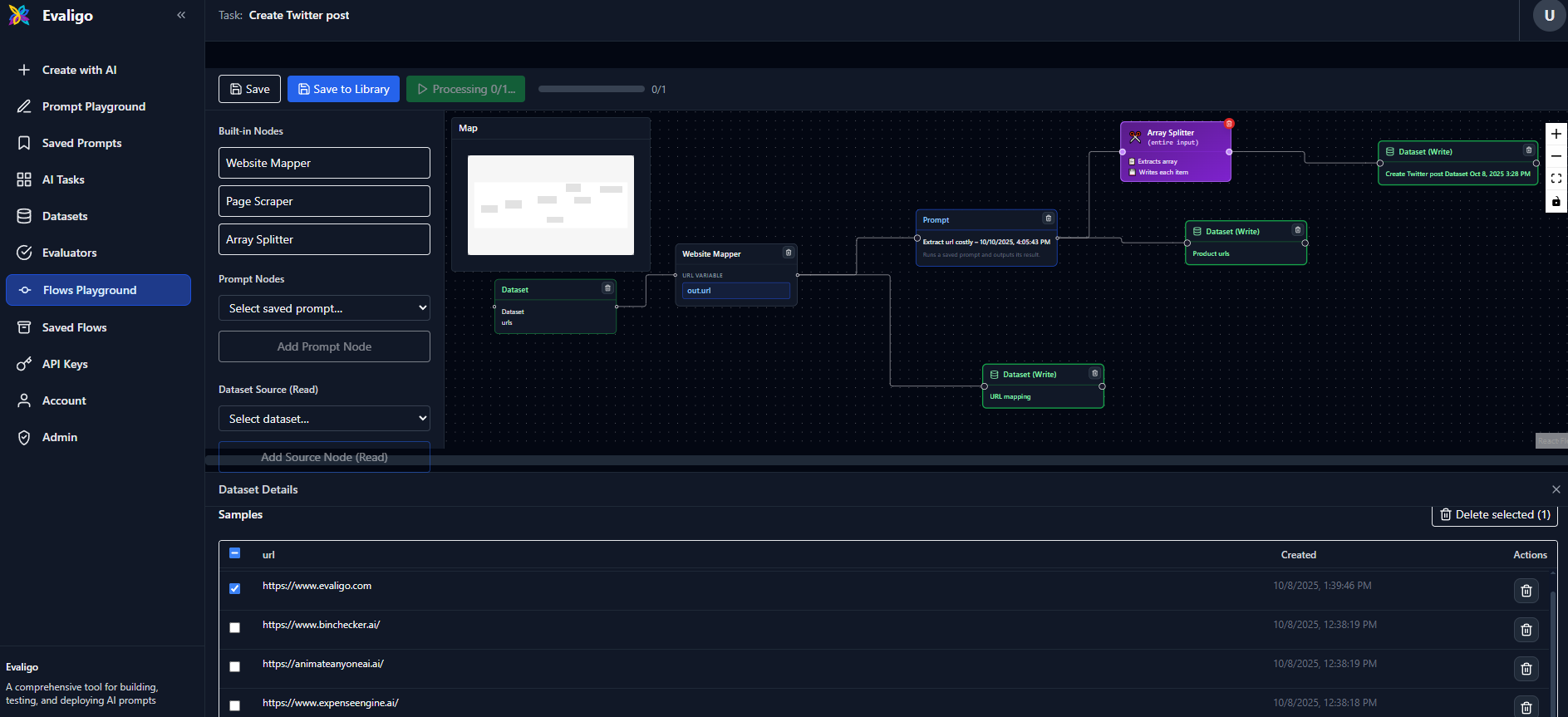
What is an AI Flow?
An AI Flow is a reusable pipeline that automates repetitive AI tasks. Think of it as a visual program where each step (node) performs a specific action, and connections define how data flows between steps.
Key characteristics:
- Visual - Build workflows by dragging and connecting nodes on a canvas
- Reusable - Save flows and run them on different datasets or inputs
- Scalable - Process single items or batch hundreds in parallel
- Deployable - Turn flows into REST APIs with one click
- Observable - Track execution, timing, and errors for every step
Core Concepts
Nodes
Nodes are the building blocks of flows. Each node performs a specific task:
- Data Sources - Read from datasets or API inputs
- Processing - Transform data, scrape web pages, or split arrays
- AI Prompts - Process data with language models using your evaluated prompts
- Data Sinks - Write results to datasets or return as API responses
Connections
Connections define how data flows between nodes. Each connection includes:
- Source - Which node and which output field (e.g.,
out,out.url) - Target - Which node and which input field (e.g.,
in,urlVar) - Mapping - Variable mappings that connect outputs to inputs
out) and the original input (_input) for pass-through. This makes it easy to access upstream data.Execution
Flows execute step-by-step, processing data through each connected node:
- 1
Select samples Choose which dataset samples or API inputs to process
- 2
Run flow The platform executes each node in sequence, following connections
- 3
Monitor progress Watch real-time progress, timing, and status for each node
- 4
Review results Check outputs in dataset sinks or API responses
Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Evaligo Flows | Zapier | n8n | LangChain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Native Nodes | ✅ Built-in prompts, evaluations | ⚠️ Basic AI integrations | ⚠️ Some AI nodes | ✅ Yes (code-first) |
| Visual Builder | ✅ Full canvas editor | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ Code only |
| Built-in Prompt Testing | ✅ A/B tests, evaluations | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⚠️ Manual |
| Web Scraping Nodes | ✅ Mapper, scraper, extractor | ⚠️ Limited | ✅ Via HTTP requests | ⚠️ Custom code |
| Dataset Management | ✅ First-class support | ⚠️ Via integrations | ⚠️ Basic storage | ❌ External only |
| API Deployment | ✅ One-click REST APIs | ✅ Webhooks | ✅ Webhooks | ⚠️ Manual deployment |
| Execution Monitoring | ✅ Real-time node-level | ✅ Task history | ✅ Execution logs | ⚠️ Custom logging |
| Learning Curve | ✅ 5-10 minutes | ✅ ~15 minutes | ⚠️ 1-2 hours | ⚠️ Days (requires coding) |
Why Choose Evaligo Flows?
- AI-first design: Unlike general automation tools, Evaligo Flows are built specifically for AI workflows with native prompt testing, evaluation, and iteration.
- Unified platform: Test prompts, build flows, and deploy APIs all in one place—no need to stitch together multiple tools.
- Smart web scraping: Purpose-built nodes for website mapping, scraping, and content extraction that work seamlessly with AI processing.
- Dataset-centric: First-class dataset support means you can easily test flows with real data, iterate, and validate quality before deployment.
- No vendor lock-in: Use your own LLM API keys (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) and maintain full control over your infrastructure.
When to Use Flows
✅ Perfect for:
- Repeatable AI tasks - Web scraping, content analysis, data extraction
- Multi-step processing - Tasks requiring 3+ sequential steps
- Batch operations - Processing hundreds of items with same logic
- API automation - Deploying AI tasks as production endpoints
- Team collaboration - Visual flows are easier to understand and share
⚠️ Consider alternatives for:
- One-off tasks - Use the Prompt Playground for quick tests
- Simple prompts - Single-step operations may not need a flow
- Complex logic - Conditional branching or loops (coming soon)
- Real-time streaming - Flows are designed for batch/async processing
Real-World Examples
1. Web Scraping Pipeline
Flow: Dataset Source → Website Mapper → Page Scraper → HTML Extractor → Prompt Analysis → Dataset Sink
Use case: Extract product features from competitor websites and analyze positioning
2. Batch Content Moderation
Flow: Dataset Source → Prompt Classification → Dataset Sink
Use case: Classify hundreds of user-generated posts for content policy violations
3. Lead Enrichment
Flow: API Input → Website Mapper → Company Info Extractor → CRM Update
Use case: Enrich leads with company information from their website
Flow Architecture
Under the hood, flows are executed as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). The platform:
- Validates the flow structure (no cycles, all inputs connected)
- Determines execution order based on dependencies
- Executes nodes in parallel where possible (future enhancement)
- Tracks state and timing for each node
- Handles errors gracefully with partial completion